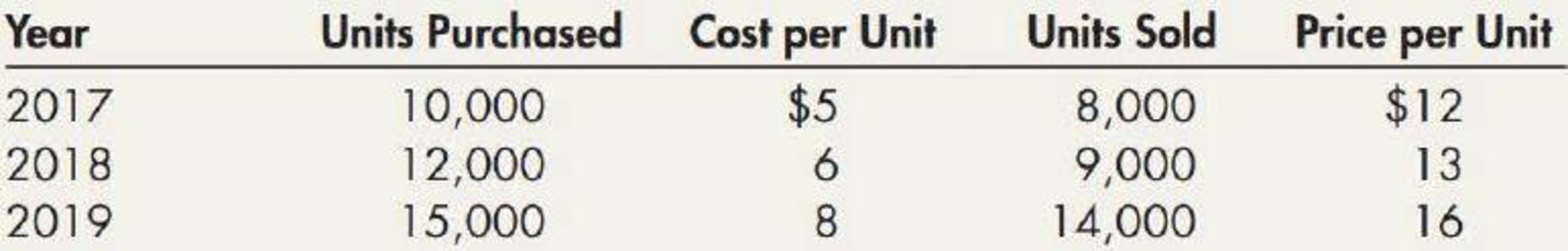
In effect, a firm is apt to sell units that may have 2000 or 2010 costs attached to them. The result is a lower cost of goods sold, higher gross margin, and higher taxes. We can see that the cost of goods sold decrease $ 4,000 after the purchasing price decrease, and it will increase the profit significantly. We can see that the cost of goods sold increase $ 4,000 just after the purchasing price increase, and it will decrease the profit significantly. LIFO Reserve refers to the difference between the inventory under the LIFO method and the inventory calculated using other methods.
- When there is a spike in the market demand or any other particular event, the older stock is consumed.
- It is not recommended for situations where stock needs to remain consistent or bulk discounts are available.
- As per this method, the current value of the inventory is first discounted to the base layer based on the current inflation rate.
- The LIFO liquidation’s effect on the cost of goods sold would affect gross income, which affects income tax, which in turn affects the operating cash flow.
Ask Any Financial Question
There are 2,000 units remaining at the end of the month, and they will value base on the old cost. There are 2,000 units (5,000 units – 2,000 units) remaining at the end of the month, and they will value base on the old cost. Many companies prefer using LIFO Liquidation as compare to the FIFO Inventory.
LIFO method When Price Decrease
As I stated in my last posting, before 1993 there were no statutory references to a liquidation bureau in the Insurance Law including the receivership article, Article 74. In 1993, subsection (g) was added to Section 7405 (Order of liquidation; rights and liabilities) requiring the superintendent as receiver to prepare an annual report on the status of each company in liquidation or rehabilitation. This allows companies to better adjust their financial statements and budget in regards to sales, costs, taxes, and profits. Last in, first out (LIFO) is a method used to account for business inventory that records the most recently produced items in a series as the ones that are sold first. That is, the cost of the most recent products purchased or produced is the first to be expensed as cost of goods sold (COGS), while the cost of older products, which is often lower, will be reported as inventory. LIFO Liquidation happens when the stock level reaches this layer, the new purchase has not yet arrived, and the company needs to deliver the old stock to the customers.

What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to getting a tax perspective by finding your effective tax rate help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Purchases at the beginning of the next year, however, could end up in next year’s ending inventory as a new LIFO layer.
» title=»Peter H. Bickford Legal & Dispute Resolution Services»>
The per-unit cost is $10 in year one, $12 in year two, and $14 in year three, and ABC sells each unit for $50. It sold 500,000 units of the product in each of the first three years, leaving a total of 1.5 million units on hand. Assuming that demand will remain constant, it only purchases 500,000 units in year four at $15 per unit. For example, when using the LIFO method for inventory accounting in periods of rising prices, the cost of reported inventory is higher than the FIFO method, which, therefore, increases a company’s cost of goods sold (COGS), decreasing its pre-tax earnings.
A copy of 11 Financial’s current written disclosure statement discussing 11 Financial’s business operations, services, and fees is available at the SEC’s investment adviser public information website – or from 11 Financial upon written request. This will happen if the units purchased during this year exceed the units sold. In other words, under the LIFO method, the cost of the most recent lot of materials purchased is charged until the lot is exhausted. PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network. This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors.
Thus when the State Comptroller sought to audit the activities of the Liquidation Bureau and issue subpoenas to Liquidation Bureau personnel, the lower court quashed the subpoenas under the Con Ed line of cases. Serio v. Hevesi, 2007 NY Slip Op (App. Div., 1st Dept., March 6, 2007). The decision can be obtained from the New York Unified Court System web site at /decisions, or by contacting me at The current administration has made a lot of noise about reforming the bureau and making it more “transparent.” It is doing this, however, by making the bureau even more permanent contrary to the mandate of Article 74 and the statutory receivership scheme. The FIFO method of evaluating inventory is where the goods or services produced first are the goods or services sold first, or disposed of first. The LIFO method of evaluating inventory is when the goods or services produced last are the ones to be sold or disposed of first.
The cost of stock, which is the last purchase, will be used to calculate the cost of goods sold. It is not related to the physical movement of the goods as it is almost impossible to track the actual inventory when we sell thousands of them. We use this method to calculate the cost of inventory sold and the valuation of the remaining stock.
A LIFO liquidation occurs when the amount of units sold exceeds the number of replacement units added to stock, thereby thinning the number of cost layers in the LIFO database. This situation can arise when management decides to retain fewer units on hand, perhaps due to a cash flow crunch. This situation can also arise when an unexpected surge in demand wipes out a large part of a firm’s inventory reserves. Because the company employs a LIFO method, the most recent layer, 2022, would be liquidated first, followed by 2021 layer and so on. This liquidation would enforce the company to match old low costs with the current higher sales prices.
